Sensor Information & Signal Processing
Forschungs- und Entwicklungsprojekte aus dem Bereich Sensorinformationsverarbeitung
 | High resolution mono- and bistatic SAR imaging by using a novel modular Radar transmitter and multichannel receiver systemThis work is the continuation of the development of radar sensors within the HITCHHIKER project. While i the first phase of this noise technology related project, the main focus was on the development of the noise transmitter system, the navigation system and the calibration devices as well as on the signal processing in half stationary SAR and on ISAR configurations, now the airborne mono- and bistatic experiments will have to be prepared and performed. | |
|
| Functional Lifting 2.0:Efficient Convexifications for Imaging and VisionAlmost all solutions of computer vision and image processing problems rely on high dimensional optimization problems. Examples are the training of neural networks in machine learning techniques, or variational methods, in which the solution is determined as the argument that minimizes a suitable cost function. | |
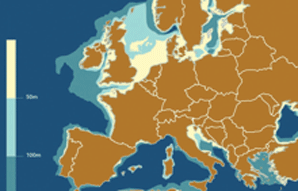
Ubiquitous Synthetic Aperture Radar ImagingThe continuous, daylight and weather independent monitoring of our environment, of our surroundings, moving objects (e.g. traffic monitoring) on ground (cars) or in the air (aircrafts) or on sea (ship and vessel monitoring) is an increasingly important and wide field of user and application interests for sustainable development, for logistics and for security and requires satellites with a permanent ubiquitously (microwave) illumination capability. Because of the extremely high operational cost for the primary radar stations currently used for air traffic monitoring, there is an urgent need for alternative technologies yielding cost-effective and global coverage. However, conventional civilian Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellites, like TerraSAR-X, TanDEM-X, COSMO-Skymed, RADARSAT-2 and SENTINEL-1 are operated in a sun-synchronous orbit which only allows daylight synchronous observation on the one hand, while the orbit time on the other is in the range of 95 min, allowing only revisit times of the same area of interest of the order of several days (as in the case of TerraSAR-X) | ||
| | Inverse Process Model with Local Model NetworksModeling of nonlinear systems based on measured data is of growing interest in the last decades. Especially in the case, that multiple input and output quantities are available, the development of physical-based models is time consuming or even infeasible. So, an alternative way has to be considered | |
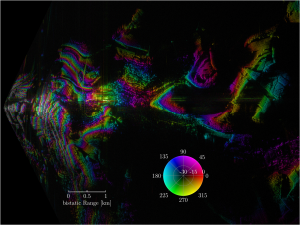 Interferometric SAR image (radar intensity and interfer-ometric phase) of Dreis-Tiefenbach/Siegen acquired by the HITCHHIKER system in 2009.and 2014 Interferometric SAR image (radar intensity and interfer-ometric phase) of Dreis-Tiefenbach/Siegen acquired by the HITCHHIKER system in 2009.and 2014 | ComSAR - | |
|
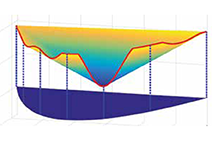
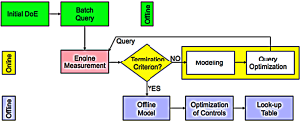
Active Learning strategy with the engine measurement as an example | Active Learning with HilomotDoEThe Design of Experiments (DoE) is used in the development and optimization of many products and processes. The experiments are used to model a functional relationship between design parameters (inputs) and the corresponding qualities (outputs) given by the process | |
 Collapsed structures after earthquake: Typical scenario for application of RAWIS warning system. © Fraunhofer FHR / Uwe Bellhäuser Collapsed structures after earthquake: Typical scenario for application of RAWIS warning system. © Fraunhofer FHR / Uwe Bellhäuser | Radar Warning and Information System (RAWIS)A „Radar-Warning and Information System for Applications in Disaster Management (RAWIS)" will be created and built up by a consortium of eight partners in order to support the emergency forces during complex cases of operations. This project is funded by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) with totally 3.6 mill. Euro within the programme „Research for Civil Security". Manager of the consortium is the Fraunhofer Research Institute for High-frequency Physics and Radar Technology (FHR), an important project partner of the Center for Sensor Systems (ZESS), hosted by the University of Siegen, i.e. professorship of Prof. Dr.-Ing. Joachim Ender. The BMBF provides financing for two scientific appointments for a period of three years.... | |
|
| Aerodynamic Optimization of Centrifugal Fans Using CFD-Trained Meta-ModelsDue to their significant contribution to the total electricity consumption of the European Union (nearly 10%), future minimum efficiency requirements for fans driven by motors with an electric input power between 125 W and 500 kW are set by EU regulations. As a consequence many currently available fans on the EU market may no longer be sold and the need for efficient design and optimization methods arises. In the context of the current project we focus on centrifugal fans..... | |
|
| AVIRO - Modular Perception System for Space RoboticsThe effective control of robots needs an exact environment model together with a current state description. The aim of AVIRO is the development of such a system. To generate a robust three dimensional model of the environment, the system can be mounted with modular sensor devices. A multi-sensorfusion combines the data of several connected units in real-time. Parallel to this, position, attitude and speed of the system are determined continuously.... | |
|
| Research Project „Dynamic Light Fields"An exciting and interdisciplinary research topic in computer graphics and computer vision is image-based rendering (IBR), where image synthesis is based on previously obtained samples of the lightfield of the scene. Previous research for IBR required static scenes or technically complex 2D camera fields, or, used geometric models requiring global optimization, as e.g. with human characters. The model assumptions in this case either strongly restricted the objects in the scene or the lighting and the reflection properties of object surfaces... | |
|
| Project Summary „PMD-Modeling"For approximately 15 years now, range measuring Time-of-Flight (ToF) camerasare under active development. One of the first approaches, the Photonic Mixing Device (PMD), was presented and prototypically implemented at the University of Siegen by Prof. Dr. Rudolf Schwarte. The PMD concept was instrumental in establishing „pmd technologies gmbh", which today is one of the world‘s leading manufacturers of ToF-cameras. The very central idea of this knowledge-transfer project is the integrated processing and conceptual integration of the topics of sensor modeling, simulation, evaluation and algorithmics for ToF cameras, on the basis of the current development status in both, the Computer Graphics and Multimedia Systems Group, as well as the industrial partner „pmd technologies gmbh".... | |
|
| Ultra high precision 3D pose estimation for 3D | |
|
a group of 3 aerial robots exploring one spot | Cooperation Concepts for Autonomous Ground and | |
| highlighting the limit area available for wind energy development in shallow water vs. areas for which deepwater solutions are required. (Source: Acciona, 1 Tech) | HiPRwind | |
 | HITCHHIKER - | |
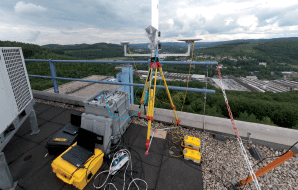 | Hitchhiker - | |
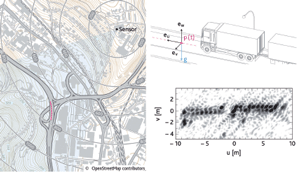
 | Robust & High Accurate Navigation Solutions for GPS-Challenged EnvironmentsRobust and highly accurate navigation systems are demanded for many applications (e.g., for robotics, automotive | |
 | Smart Intelligent Aircraft Structures -SARISTU
| |
| | „Subsurface Imaging“ | |
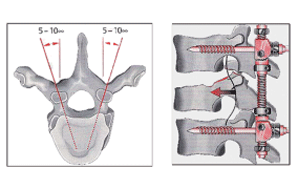 | Robot-based surgical assistance system for spine applications
| |
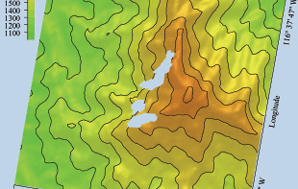
| scene. The elevation data provided by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) are used as reference and potentially as additional information to be processed by the Kalman filter. | Sensing the Earth‘s Third Dimension | |
 Scene Analysis (Seismic sensors and Radar sensors) Scene Analysis (Seismic sensors and Radar sensors) | Long-range Scene Analysis with Time-of-Flight CamerasObject recognition and tracking are the main tasks in computer vision applications such as safety, surveillance, | |
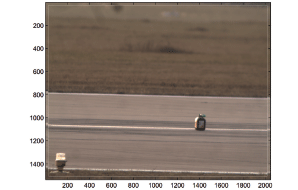 | Development and Investigation of a Long/Medium-Range Time-of-Flight and Color Imaging SystemIn this work, medium and long-range lighting devices working together with a 2D/3D scanner-camera were Download PDF | |
|
Vision of an aircraft, similar to the human nervous system, completely equipped with sensors. Source: EADS | Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Phenomena for the Optimal Design of Multi-Sensoric Monitoring SystemsMaintenance costs have a big share of the total life cycle cost of a modern aircraft in addition to manufacturing and fuel cost. | |
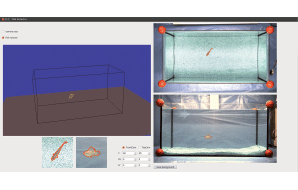 | Analysis-by-synthesis with Virtual Fishes as an Experimental Method for Mate-choice studiesIn June 2012 the interdisciplinary, DFG-funded project of the Institute of Real Time Learning Systems (EZLS), led by Prof. Kuhnert and the Department of Biology and Didactics, led by Prof. Witte, started. The project consists of two parts. EZLS analyses fish's movements and behaviour with help of a computer vision system. The gathered information is used in the sequel to create a photo-realistic simulation of fishes and it behaviour. | |
|
| High resolution mono- and bistatic SAR imaging by using a novel modular Radar transmitter and multi-channel receiver SystemThe project pursues the goal of extending and enhancing the multi-channel SAR receiver system currently developed at the Center for Sensorsystems to a complete bi- and monostatic SAR sensor, respectively. The enhancement essentially comprises the development and design of a novel modular transmitter, capable to flexibly change the transmitted signal‘s waveform on a pulse to pulse basis between broadband deterministic or stochastic signals.... | |
|
| Segmentation and Classification of High Resolution SAR ImagesThis project is part of a cooperation of the Center for Sensorsystems with the Institute of Electronics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IECAS). Hereby the work of a doctoral scholarship holder of the MOSES programme in the field of remote sensing is funded. The main issue of the project is to build up an algorithm to automatically perform land cover classification. Another issue is buildings extraction over urban areas by using high resolution SAR images. The algorithm framework will not only compare features (e.g. texture feature, image intensity value, etc.), but also integrate statistical learning algorithms (e.g. probabilistic graph model, Bayesian parametric method, Bayesian nonparametric method, etc.). Furthermore, a suitable approximate inference technique will be chosen. In this way will combine machine learning algorithms with feature based ones for performing SAR image characterization..... | |
|
| Thermoscan - Energy Efficiency Improvement Of Buildings With Large Area High Resolution ThermographyIn times of increasing energy costs, the thermal insulation of houses becomes a central and important role. Especially older buildings have a high potential for savings. Thermal bridges like shutter boxes, warped window frames or humid walls cause a loss of heat. To economize thermal energy these points need to be detected. Very suitable for this task are infrared cameras. Those systems create pseudocolor images that reflect the surface temperatures of objects in the scene. One main disadvantage is the poor optical resolution. Even expensive professional units have less than one mega pixel which is low compared against current visual cameras..... | ↑ |