Research
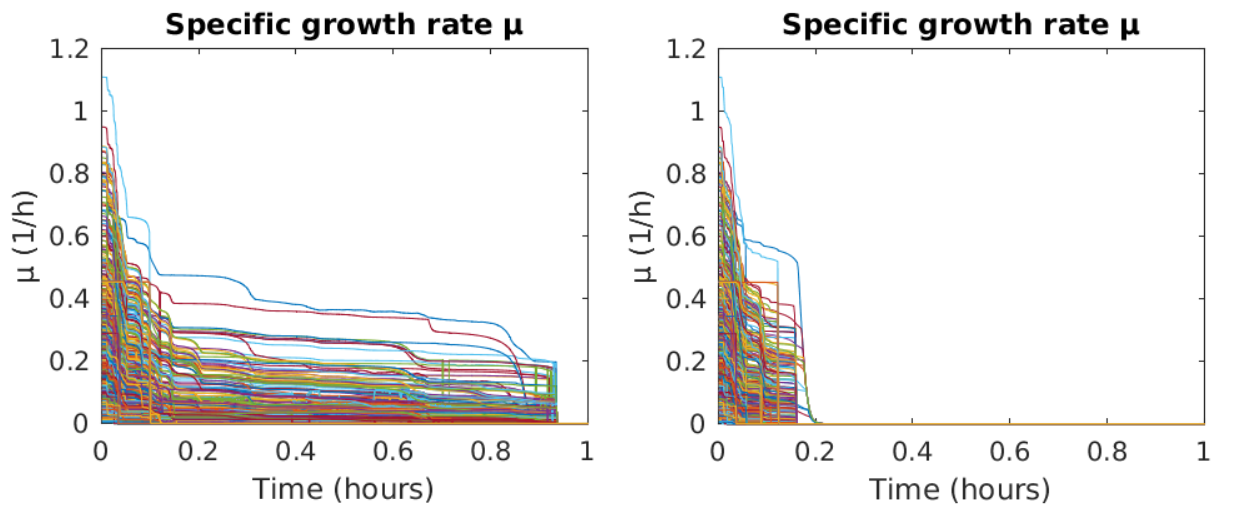
The human body is inhabited by microbiomes in many locations, and their influence on human wellbeing and health is becoming more and more apparent. For example, changes in the composition of the gut microbiome have been observed in many diseases, ranging from inflammatory bowel disease to neurodegenerative diseases. Mechanistic explanations for such observed correlations are often missing and difficult to establish due to the multitude of factors acting concurrently upon microbiomes. In this context, we develop mechanistic modeling approaches which enable the formulation of hypotheses regarding underlying mechanisms explaining observed microbiome dynamics and microbiome-host interactions. Furthermore, intervention strategies can be devised to steer complex microbiomes towards desired states. Moreover, within computer simulations, individual factors and processes can selectively be modified, elucidating their importance for overall dynamics. The close physical proximity of microbial cells within microbiomes enable a multitude of interactions to unfold, determining their functioning and dynamics. Focussing on the exchange of compounds for example, simulations show that this process, after an initial phase of fast growth, is enabling a second long phase of slow growth (Figure 1). In order to generate experimental data necessary for modeling, we will establish a sequencing lab enabling the recording of microbiome composition, metabolic potential, and activity using next-generation-sequencing.
Figure 1: Simulating the digestion of a food pulse by a microbiome comprising over 700 microbial species. An initial phase of fast growth is followed by an extended period of slow growth until growth ceases for all microbial populations close to 1 h (left). If the exchange of metabolites is prohibited in the simulation, the second phase of slow growth vanishes (right). |