Development of natural product derivatives for fluorimetric DNA detection in cells
Project title: Development of natural product derivatives for fluorimetric DNA detection in cells
This project deals with the development of fluorescent probes based on natural products for the detection of nucleic acids. In particular, the underlying structures of natural products are employed to support the required biocompatibility for DNA detection in cells. For this purpose, the basic structures of protoberberine and β-carboline alkaloids are modified in such a way that the resulting derivatives have a very low fluorescence intensity, which increases characteristically when binding to DNA, thus enabling the targeted fluorimetric analysis.
So far, the following results were obtained.
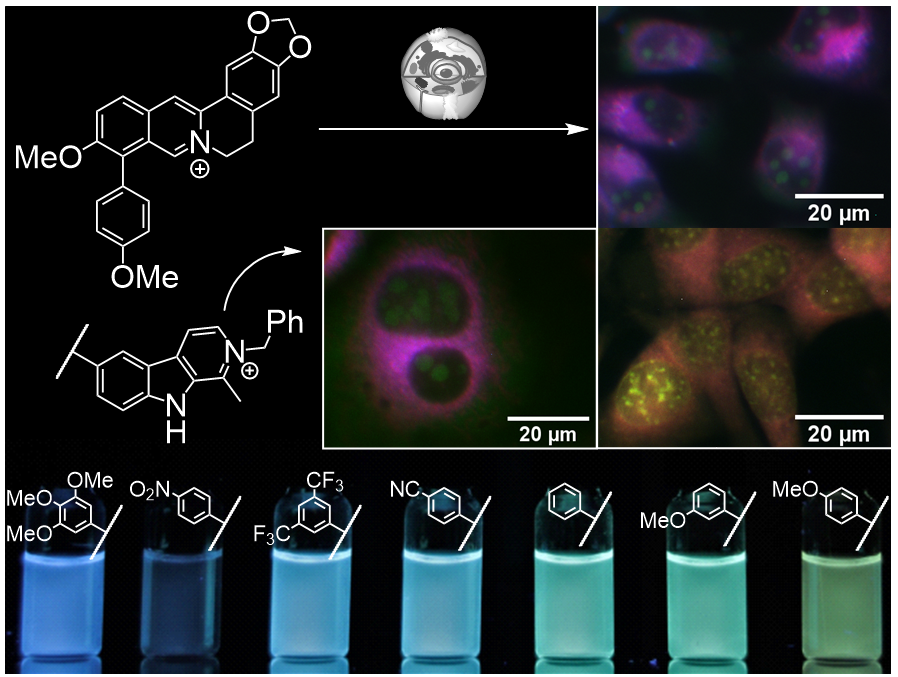
Berberine and harmane scaffolds were functionalized at different positions, and the most promising derivatives of these series were further investigated as probes for fluorimetric cell analysis. Specifically, aryl-substituted derivatives showed low fluorescence quantum yields because of a deactivation of the excited state by rotation around the biaryl axis. In turn, the emission intensity increased upon complexation with DNA, mostly pronounced with methoxy-substituted derivatives. The latter enabled the staining of nucleoli in eukaryotic cells. Notably, one berberine derivative exhibited a fluorescence light-up effect exclusively in the nucleus in fixed cells, so that it may be used as indicator dye for cell death. In contrast, an amino-substituted berberine derivative showed pH- and DNA-dependent fluorescence. Namely, its low emission intensity did not increase upon association with DNA at neutral conditions, whereas at pH 5 a fluorescence light-up effect resulted from association with quadruplex DNA.
Series of the coralyn-related quinolizinium ions were also investigated as multifunctional fluorescent probes. A dimethylamino-substituted derivative was identified that is non-fluorescent in buffer solution, but exhibited different light-up effects upon association with duplex DNA, quadruplex DNA, RNA, and BSA, which enabled the fluorimetric differentiation between these analytes. Hence, this dye was employed for the analysis of the cell nucleus by epifluorescence and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM). Likewise, the characteristic emission properties of an aminoquinolizinium were released by the reaction of the non-fluorescent nitro-substituted precursor with nitroreductase. This fluorogenic reaction in the enzyme binding site was exemplarily utilized for the fluorimetric detection of reductase activity in E. coli and may thus be used to determine the hypoxia status of cells.
Steady-state and time-resolved photophysical studies of hydroxy-substituted harmane derivatives showed that these compounds can be used for the fluorimetric monitoring of probe-water interactions. However, the detailed analysis of water dynamics, in particular in the microenvironment of DNA, cannot be performed with these dyes as they do not provide the required delicate balance between ground and excited-state acidity, photophysical properties, and DNA binding.
Publications:
1. P. Groß, S. I. Druzhinin, H. Schönherr, H. Ihmels, ChemPhotoChem, zur Publikation angenommen. Spectroscopic investigation of the quadruplex DNA-binding properties of 9-aryl-substituted isoquinolinium derivatives. EarlyView: https://doi.org/10.1002/cptc.202400241
2. P. Groß, H. Ihmels, J. Fluoresc. 2024, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-024-03691-z. Studies about the effect of halogenated solvents on the fluorescence properties of 9-aryl-substituted isoquinolinium derivatives – A case study. DOI: 10.1007/s10895-024-03691-z
3. P. Groß, P. M. Pithan, H. Ihmels, ARKIVOC 2023, 202312110. RhIII-catalyzed synthesis and investigation of the DNA-binding properties of 11- and 13-substituted berberine derivatives. DOI: 10.24820/ark.5550190.p012.110
4. P. Groß, R. S. Hoffmann M. Müller, H. Schönherr, H. Ihmels, ChemBioChem 2023, e202300761. Fluorimetric cell analysis with 9-aryl-substituted berberine derivatives as DNA-targeting fluorescent probes. DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202300761
5. P. Groß, R. S. Hoffmann M. Müller, H. Schönherr, H. Ihmels, ChemistryEurope 2023, 1, e202300045. 6-Aryl-substituted harmanium derivatives as light-up probes for fluorimetric DNA detection and staining of eukaryotic cells. DOI: 10.1002/ceur.202300045
6. P. Groß, H. Ihmels, J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 4010. Synthesis of fluorescent, DNA-binding benzo[b]indolonaphthyridinium derivatives by a misguided Westphal condensation. DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c02755
7. P. J. Wickhorst, H. Ihmels, M. Marianne Lammert-Baumgartner, M. Müller, H. Schönherr, New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 39. 9-Nitrobenzo[b]quinolizinium as Fluorogenic Probe for the Detection of Nitroreductase in vitro and in Escherichia coli. DOI: 10.1039/D1NJ05230F
8. P. J. Wickhorst, S. I. Druzhinin, H. Ihmels, M. Müller, M. S. Sardo, H. Schönherr, G. Viola, ChemPhotoChem, 2021, 5, 1079. A dimethylaminophenyl-substituted naphtho[1,2-b]quinolizinium as multicolor NIR probe for the fluorimetric detection of intracellular nucleic acids and proteins. DOI: 10.1002/cptc.202100148
9. P. J. Wickhorst, H. Ihmels, Molecules 2021, 26, 2566. Berberrubine phosphate: A selective Fluorescent Probe for Quadruplex DNA. DOI: 10.3390/molecules26092566
10. P. J. Wickhorst, M. Blachnik, D. Lagumdzija, H. Ihmels, Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 991. Synthesis of 10-O-Aryl-Substituted Berberine Derivatives by Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling and Investigation of their DNA-Binding Properties. DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.16.230
11. P. J. Wickhorst, H. Ihmels, Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 8580. Selective, pH-Dependent Colorimetric and Fluorimetric Detection of Quadruplex DNA with 4-Dimethylamino(phenyl)-Substituted Berberine Derivatives. DOI: 10.1002/chem.202100297
