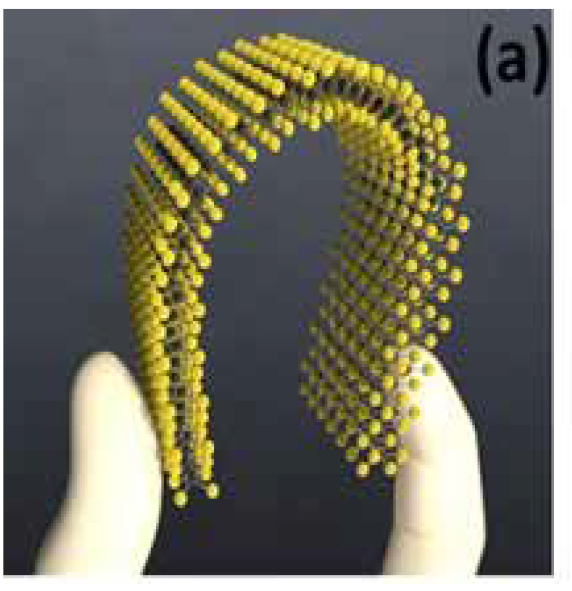
 | HEA2D – Production, function and application of 2D-Nanomaterials HEA2D is a collaborative project between two Universities (University of Siegen, University of DuisburgEssen), a research institute (Fraunhofer Institute for Production Technology, Aachen) and three industrial partners (Aixtron, Coatema Coating Machinery and Kunststoff-Institute Lüdenscheid). The goal of the project is to develop a scalable technology for electronic and optoelectronic components based on flexible twodimensional materials for potential applications in the automotive industry, in particular integrated into plastics. We envision touch elements, photodetectors and light emitting diodes based on two-dimensional (2D) materials to be integrated into automotive parts like the dashboard using low-cost manufacturing technologies. Download PDF | | |

THz CMOS camera chip housing | LumiCS -
Terahertz illumination concepts for reciprocal
compressive imaging in silicon technologies The project’s main objective is to leverage silicon-based technologies for a breakthrough in terahertz (THz) compressive imaging. This interdisciplinary research
project combines natural sciences with engineering sciences to realize a highly sensitive real-time THz imaging system without the need for mechanical scanning.
The key innovation of LumiCS is an active Terahertz Digital Light Processor (T-DLP) fully integrated in a silicon process technology. Download PDF | |
| 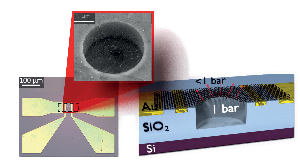
S. Wagner, C. Weisenstein, A. D. Smith, M. Östling, S. Kataria, and M. C. Lemme, “Graphene transfer methods for the fabrication of membrane-based NEMS devices,” Microelectronic Engineering, vol. 159, pp. 108–113, Jun. 2016. | NanoGraM - Graphene Fabrication, Integration and
Metrology for Nanoelectromechanical Systems This project is a cooperation of the group of Graphene- based Nanotechnology, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Siegen and four industrial partners (Infineon Technologies AG, WITec GmBH and Spanish SMEs Graphenea and SIMUNE). The goal of the project is to explore new
Nano-/Microelectromechanical (NEMS/MEMS) devices
based on graphene. Download PDF | |
| 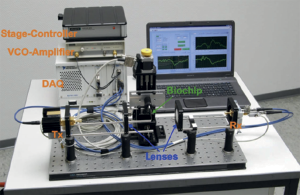
Biochip reader setup operating at a frequency of approximatedly 250 GHz. | Ultrasensitive marker-free biomolecular THzdetection
for tumor related analytics: PCR-free
sensitivity, biomolecular extension and biological
relevance Genomics and proteomics hold promise to revolutionize future health care, targeting profound novel visions like predictive, preventive and personalized medicine.
The enormous advance in these fields is closely coupled to the development of powerful, reliable and efficient methods to detect, identify and analyze biomolecules and their complex interaction networks. In the last decades techniques have continuously improved, providing a plethora of information for biomolecular function. Current progress is changing from “observing” dependencies, towards “understanding” mechanisms in their full interaction Network. Download PDF | |
| 
Vision of an aircraft, similar to the human nervous
system, completely equipped with sensors.
Source: EADS | Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Phenomena for the Optimal Design of Multi-Sensoric Monitoring Systems Maintenance costs have a big share of the total life cycle cost of a modern aircraft in addition to manufacturing and fuel cost.
In this context, structure-healthmonitoring systems (SHM-systems) have been integrated into aircrafts to detect early damage and to monitor efficiently the health of the structure. Download PDF | |
 | Smart Intelligent Aircraft Structures -SARISTU
SARISTU (Smart Intelligent Aircraft Structures) is a large-scale integrated project which aims at achieving
reductions in aircraft weight and operational costs, as well as an improvement in the flight profile specific aerodynamic
performance. Coordinated by Airbus, the SARISTU Consortium brings together 64 partners from
16 European countries. The total budget of the project is 51 M€, partially funded by the European Commission
under FP7-AAT-2011-RTD-1 (Grant Agreement number 284562). The project started in September 2011 and is
expected to be completed by August 2015.
Download PDF | |
| 
3D-model of planned demonstrator | RF2THzSiSOCFrom
RF to MMW and THz Silicon SOC Technologies
Goal of RF2THzSiSOC project is the establishment of silicon technology platforms for emerging Radio Frequency
(RF), Millimeter-Wave (MMW) and Terahertz (THz) consumer applications such as: 77GHz/120GHz
automotive radars, MMW Imaging and Sensing, fast measurement equipment, 60GHz wireless networking
and fast downloading transmitter(Tx)/receiver(Rx), 400Gbit/s optical data communications, 4G photonic
mobile communication transceiver and RF wireless communication requiring high performance devices
(transmitted power, consumption, integration, isolation), as well as two-way satellite communication
systems. Moreover it targets at the creation of a platform for various MMW and THz applications from different
disciplines like health science, material science, genetic screening, security, industrial automation.
Download PDF | |
 | Interactive Analysis of Multi-modal Confocal
Raman Microscopy Data The DFG-project “Interaktive multifunktionelle konfokale Bildanalyse” involves the analysis and visualization
of the measurement data obtained from our multispectral confocal Raman microscopy system.
Specifically, the motivation of the project is to detect constituting components and physical structure of the
specimen and present the results in a concise and intuitive manner. Download PDF | |
| 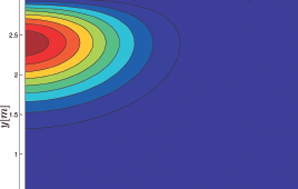 Cross section of a thin glass sheet with integrated
graded index waveguides manufactured by an ion
exchange process | Micro Optical Components:
Efficient Manufacturing by Ion Exchange Processes´ During the last 10 years the research group of Prof. Griese has been working intensively on the development
of a novel hybrid electrical-optical interconnection technology on the printed circuit board Level. Download PDF | |
 | HITCHHIKER -
Bistatic Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging
with a Stationary Passive Receiver System To develop efficient algorithms for bistatic SAR focussing, there is a need for test data sets. Therefore it was
decided to build up an own affordable sensor system to perform bistatic SAR experiments. Because of the high
operating cost of a moving sensor platform, a stationary receiver was considered. Download PDF | |
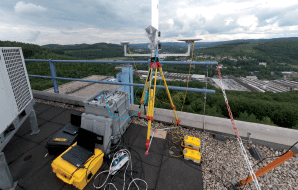 | Hitchhiker -
Multi Channel SAR Sensor Continuing the microwave based bistatic imaging line, the Hitchhiker system is being upgraded to a fully operational
flexible multi waveform interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging system. Designed in
2009, Hitchhiker was initially a purely passive bistatic receiver system working with TerraSAR-X microwave
illumination with two coherent channels, one channel for the direct signal of the transmitter and another one
for scene echoes. Download PDF | |
| 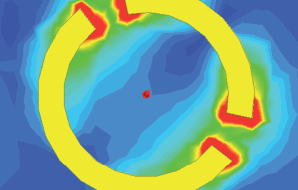 Simulation of the electrical field from one structure element
of the sensor chip | EIFFEL
Early invasive fungal infection detection with Terahertz sensor systems Due to medical advances in fields of transplant technology and cancer therapy these procedures now come
on in daily clinical life. These interventions or therapies require the suppression of the patient’s immune
system. So the patient becomes susceptible to infections of any kind. At this point Invasive-Fungal-Infections
(IFI) are a serious health problem. Download PDF | |
| 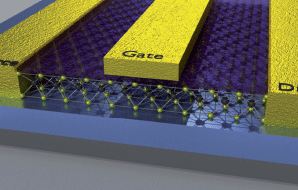
Schematic of a MoS2 field effect transistor | Two-dimensional materials - a new playing ground for engineers Graphene is a two-dimensional (2D) crystal made up of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice. It is
only one atomic layer thick, which makes it the thinnest material known to exist. Graphene also happens
to be the strongest material, an excellent conductor for both electric current and heat, highly transparent and
very flexible and stretchable. Download PDF | |













